The 2021 Global Health Security Index, released in mid December 2021, ranks 195 countries according to their capacity to respond to epidemics and pandemics, as assessed by John Hopkins Centre for Health Security, at Johns Hopkins University Bloomberg School of Public Health, and experts from numerous countries.
The world remains unprepared for future epidemic and pandemic threats. Countries across all income levels remain dangerously unprepared to meet future epidemic and pandemic threats, according to the new 2021 Global Health Security (GHS) Index released December 8, 2021.
The world’s overall performance on the GHS Index score slipped to 38.9 (out of 100) in 2021, from a score of 40.2 in the GHS Index, 2019.
This, even as infectious diseases are expected to have the greatest impact on the global economy in the next decade.
More than 80% of countries have no plan for distributing vaccines or medications during an emergency, while 70% lack sufficient capacity hospital capacity, clinics and health centers, the report found.
Although many nations have funnelled resources into addressing the acute COVID-19 crisis, few have made dedicated investment to improve overall emergency preparedness.
In 2021, no country scored in the top tier of rankings and no country scored above 75.9, the report showed.
The document was jointly released by non-profits Nuclear Threat Initiative (NTI) and the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security.
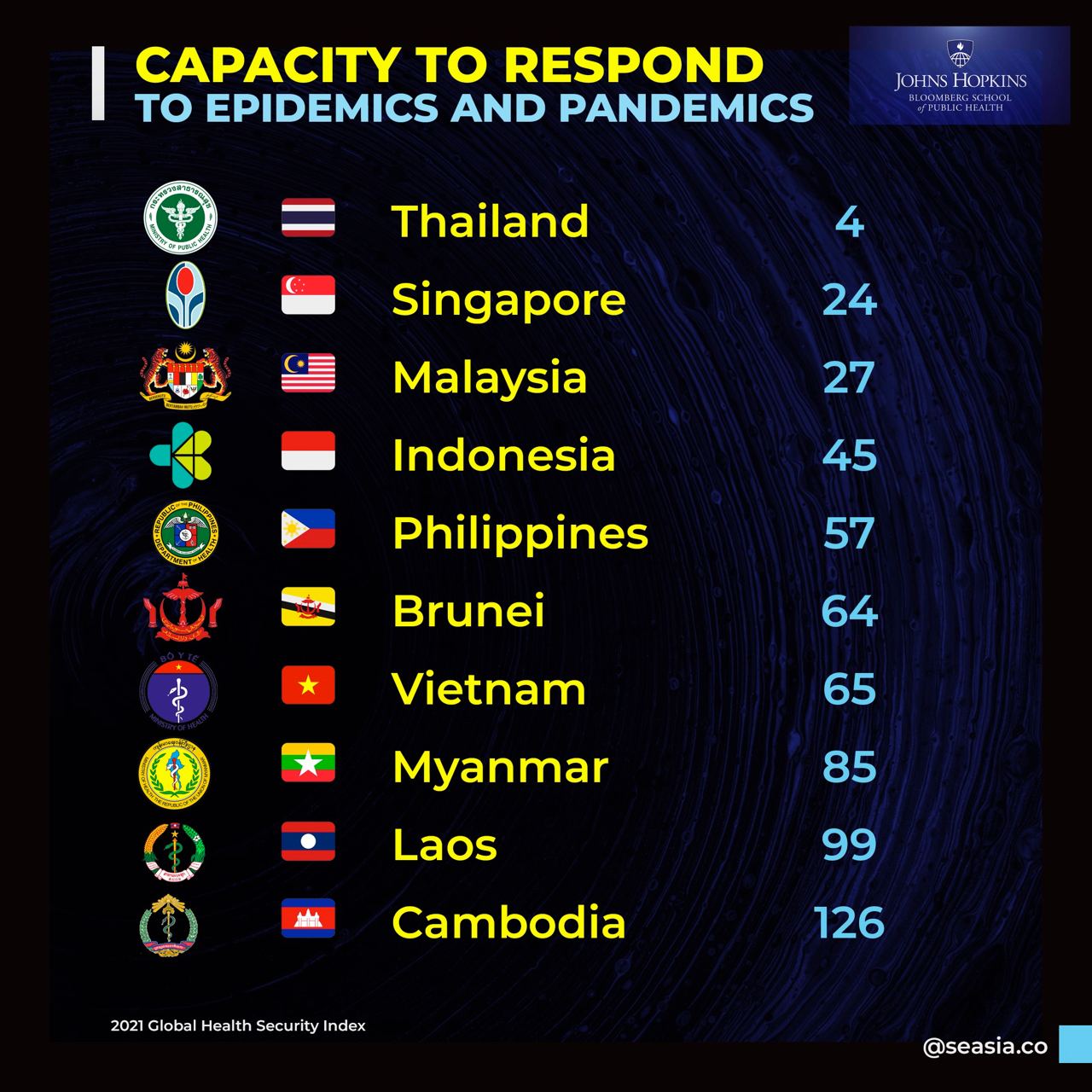
All countries had insufficient health capacities. This left the world acutely vulnerable to future health emergencies, according to the Index that measured the capacities of 195 countries to prepare for epidemics and pandemics
Sixty-five per cent of assessed countries had not published and implemented an overarching national public health emergency response plan for diseases with epidemic or pandemic potential.
Seventy-three per cent countries did not have the ability to provide expedited approval for medical countermeasures, such as vaccines and antiviral drugs, during a public health emergency.
Thus, the world was acutely vulnerable to health emergencies in the future. These included pandemics that could be much more devastating than the novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19), the second edition of the GHS Index, said.
The findings of the GHS Index 2021 are based on a revised framework and updated data collection conducted between August 2020 and June 2021.
It has assessed countries across six categories, 37 indicators and 171 questions, using instantly available information.
Most countries, including high-income ones, have not made dedicated financial investments in strengthening epidemic or pandemic preparedness, according to the GHS Index 2021.
Close to 79 per cent of the 195 countries assessed had not allocated national funds within the past three years to improve their capacity to address epidemic threats, it found.
In fact, just two low-income countries have allocated funds. Some 90 countries have not fulfilled their full financial contribution to the World Health Organization. Fourteen of these are high-income countries.
Just one-fourth of the countries considered in the Index have published an updated health workforce strategy over the past five years to address the shortage of health work force.
Health emergencies demand a robust public health infrastructure with effective governance. But the trust in government, which has been a key factor associated with success in countries’ responses to COVID-19, is low and decreasing, the index noted.
A whopping 82 per cent of countries have low to moderate levels of public confidence in their government, according to the Index.
The world’s performance on communicating the risk communication messages to people has also been very disappointing.
Over 71 per cent of the countries did not identify how risk communication messages would reach populations and sectors with different communication needs related to language, location and media reach.



















