What is a trench? An ocean trench is a narrow, elongated depression found on the ocean floor, recognized as the deepest part of the Earth’s surface. According to the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, ocean trenches are formed through the process of subduction, where two or more tectonic plates converge.
In this process, the older, denser plates are pushed beneath the lighter ones, diving deep into the Earth's layers. This results in the bending of the ocean floor and the formation of a V-shaped, steep depression. These depressions are known as ocean trenches.
Among the many ocean trenches worldwide, the Mariana Trench stands out as the deepest. Not only is it a remarkable geological feature, but it also remains a vast, unexplored frontier for marine research and a natural wonder for scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Location and Depth of the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is located in the western Pacific Ocean, east of the Philippines and south of Japan. Its deepest point, known as Challenger Deep, reaches a depth of approximately 10.935 meters (35,843 feet).
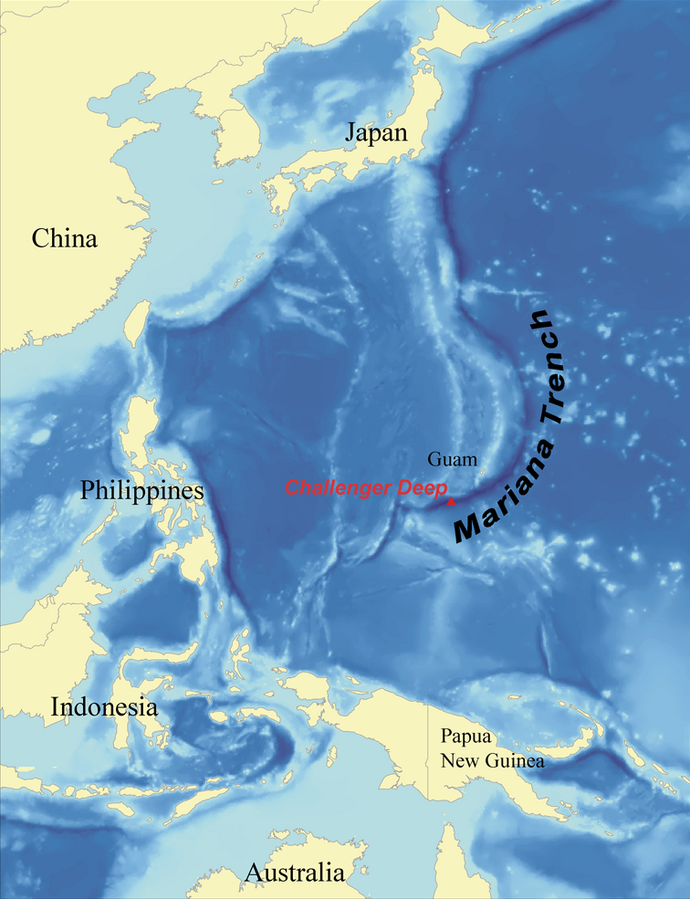
To put this into perspective, Mount Everest, the highest mountain on Earth at 8.849 meters, could be submerged entirely in the Mariana Trench, and its peak would still remain about 2 kilometers below the ocean's surface.
This dramatic contrast between the deepest and highest points on Earth emphasizes the extreme nature of the trench and highlights the vastness of the ocean’s uncharted territories.
Life in Extreme Depths
Despite its extreme conditions of total darkness, high pressure, and near-freezing temperatures, life exists in the Mariana Trench. Species adapted to the trench’s unique environment, including deep-sea fish, giant amoebas, and specially evolved bacteria, thrive in these conditions.
These organisms have adapted to the immense pressure and lack of sunlight, creating an extraordinary ecosystem unlike any other on Earth.
The trench also houses various microbial ecosystems that offer valuable scientific insights. These unique ecosystems are studied for potential discoveries, such as new antibiotics and biotechnological applications, that could be beneficial for human health.
The History of Mariana Trench Exploration
The exploration of the Mariana Trench began in the mid-20th century. In 1960, Jacques Piccard and Don Walsh were the first humans to reach the Challenger Deep, aboard the Trieste submersible.
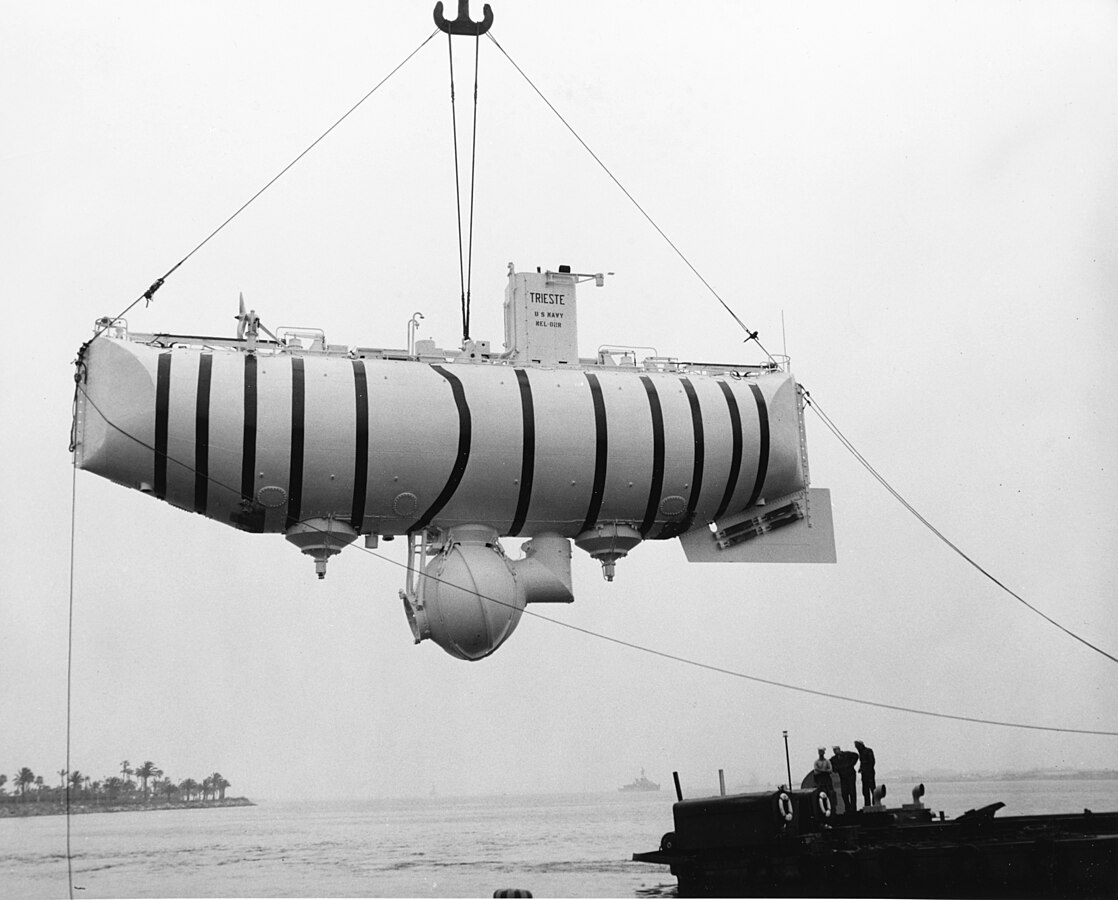
Since then, several deep-sea expeditions have been undertaken using submersibles and robotic systems, including the famous solo expedition by filmmaker James Cameron in 2012.
These expeditions not only showcase the technological advancements required to withstand such extreme pressures but also open doors to studying life, geology, and environmental conditions at one of the most inaccessible parts of the Earth.
Comparing with Mount Everest
The Mariana Trench is often compared to Mount Everest to put its depth into perspective. Everest, at 8,848 meters, is the highest point on land, but Challenger Deep in the Mariana Trench is more than 2 kilometers deeper than Everest’s peak.
If Everest were placed at the bottom of the trench, its summit would still be submerged by water. This stark contrast between Earth’s highest and deepest points provides a striking reminder of the vastness and mystery of our planet’s oceans.
Why Mariana Trench Matters
Mariana Trench is more than just the deepest point on Earth. It plays a crucial role in global biogeochemical cycles, such as carbon storage and nutrient distribution in marine ecosystems. It is also a natural laboratory for studying the extreme conditions that can support life. The trench’s existence underscores the remarkable adaptability of life and highlights the unknown potentials still hidden in our oceans.
Exploring the trench not only allows scientists to gain knowledge about life, geology, and oceanography, but it also raises awareness of the fragility of marine environments. As humans continue to explore and exploit the ocean’s resources, we must also prioritize preserving these critical ecosystems and ecosystems like the Mariana Trench.
The Mariana Trench serves as a reminder of the mysteries that still lie beneath the ocean's surface. From its extreme depth to the unique life forms it houses, the trench represents the last frontiers of human exploration and knowledge.
Our understanding of the trench continues to expand, but there is still much to uncover about the ecosystems and geologies that thrive in such hostile conditions. The Mariana Trench not only holds answers to some of the Earth’s most profound mysteries but also offers the potential for groundbreaking scientific discoveries that could benefit the world for generations to come.


















