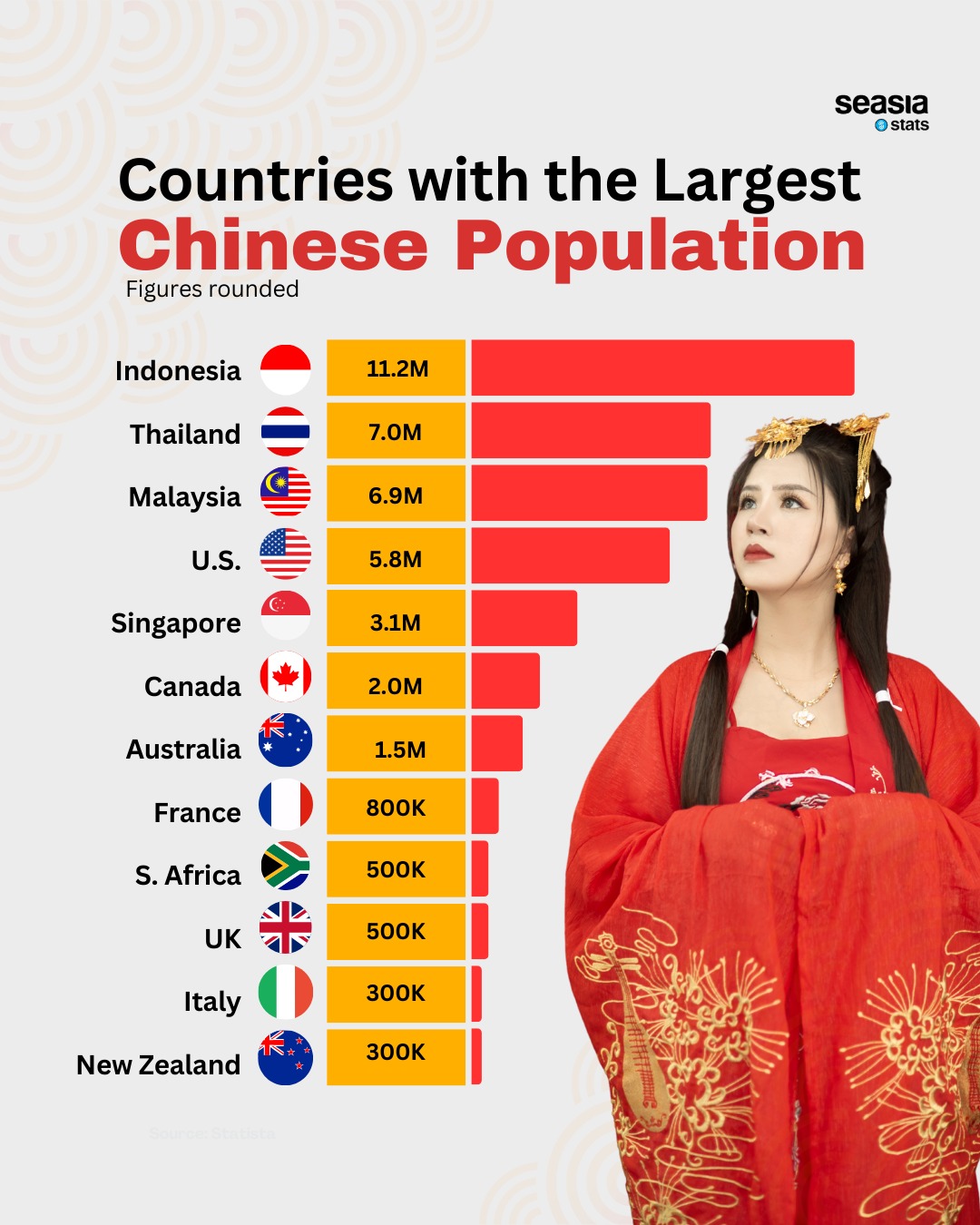
The Chinese diaspora represents one of the largest and most influential communities worldwide, with significant concentrations in Southeast Asia and beyond. Drawing on data from Statista, this overview highlights the top 12 countries with the largest overseas Chinese populations, excluding China itself.
Southeast Asia: Historical and Cultural Ties
Southeast Asia hosts some of the largest Chinese communities, shaped by centuries of migration and cultural exchange. Indonesia stands out as a prominent example, with a significant Chinese population contributing to its economy, politics, and culture. These communities largely descend from Chinese immigrants who arrived generations ago, forming a deeply rooted presence in countries like Malaysia, Thailand, and the Philippines.
The integration of Chinese culture into Southeast Asian societies is evident in shared festivals, cuisines, and entrepreneurial ventures. Despite historical challenges, these communities have played pivotal roles in fostering regional connectivity and economic growth.
Western Countries: Recent Immigration Trends
In contrast to the long-established Chinese communities in Southeast Asia, Western nations such as Australia, Canada, and the United States have seen a more recent influx of Chinese immigrants. These migrations are often driven by education, economic opportunities, and political stability.
The trend is particularly pronounced among high net worth individuals (HNWIs) from China. In 2023 alone, over 13,000 HNWIs emigrated, favoring destinations like the U.S., Canada, and Singapore. These individuals, defined as having at least $1 million in liquid financial assets, bring significant economic contributions to their host countries.
The HNWI Exodus from China
China is not the largest source of global emigrants—ranking behind India and Mexico—but it leads in the number of HNWIs leaving the country. This outflow is projected to rise sharply, with 15,200 HNWIs expected to emigrate in 2024, marking the highest recorded exodus.
The factors driving this trend include China’s slowing economic growth, challenges in the real estate market, and heightened regulatory scrutiny. These issues have led many affluent Chinese to seek opportunities abroad, contributing to a growing Chinese presence in global hubs.
A Diverse Global Influence
The overseas Chinese population reflects a complex tapestry of historical migration and modern globalization. While Southeast Asia continues to host well-established Chinese communities, recent trends in HNWI migration underscore the evolving dynamics of Chinese influence worldwide. This dual legacy of rootedness and mobility underscores the significant role the Chinese diaspora plays in shaping the economies and cultures of their host countries.