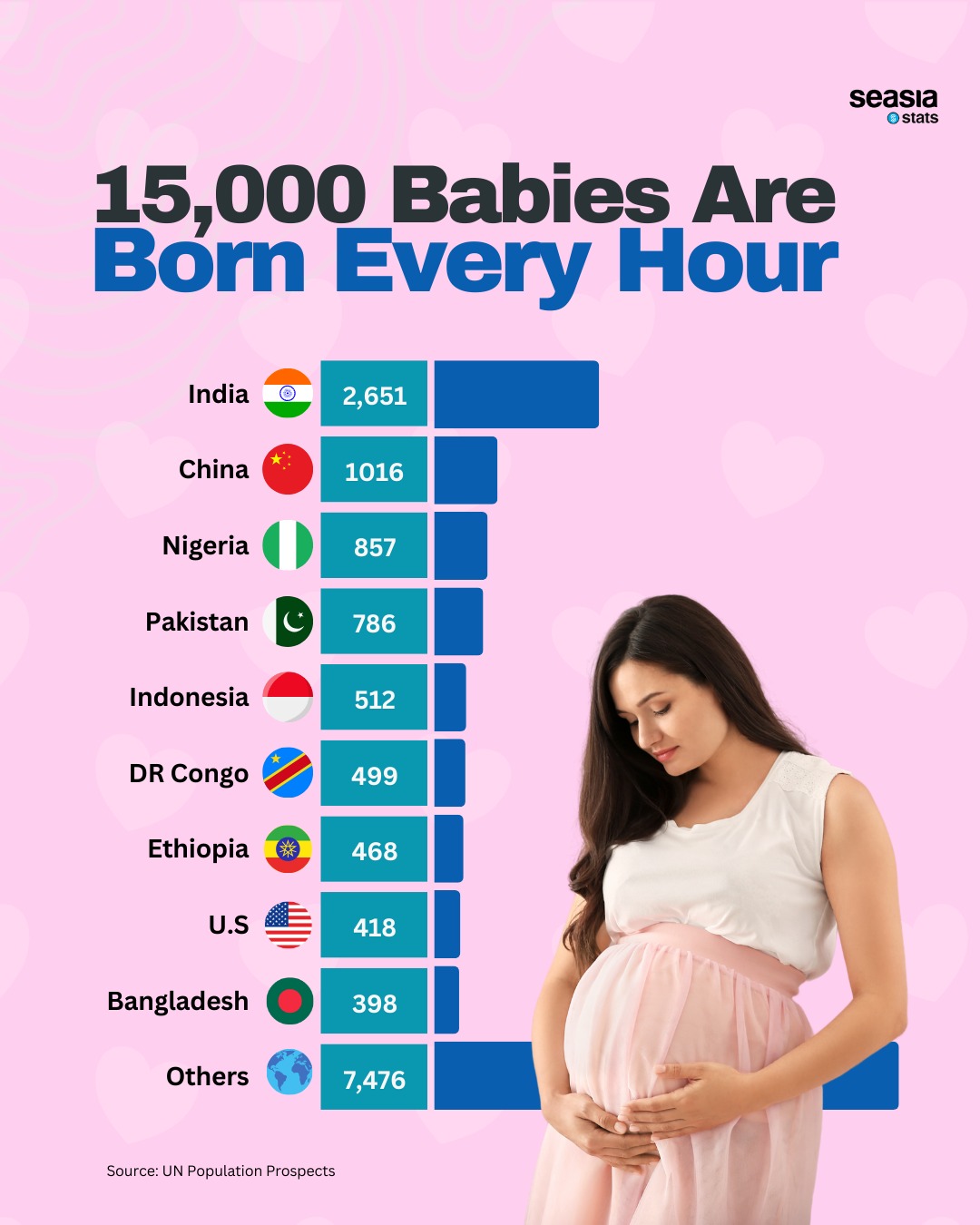
Global population growth continues to capture attention, with a recent visualization offering insights into where the highest birth rates are concentrated in 2023. Based on data from the UN Population Prospects, the chart ranks countries by the number of babies born per hour, revealing intriguing trends about population dynamics worldwide.
Geographic Concentration of Births
Remarkably, half of all babies born globally each hour are concentrated in just nine countries. These nations include India, China, Nigeria, Pakistan, Indonesia, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DR Congo), Ethiopia, the United States, and Bangladesh.
The dominance of these countries highlights the geographic concentration of global population growth. Their combined populations and high birth rates play a critical role in shaping demographic trends, particularly in Asia and Africa, which lead in the number of births.
Asia and Africa at the Forefront
Of the nine countries, five are located in Asia—India, China, Pakistan, Indonesia, and Bangladesh—while three are in Africa—Nigeria, DR Congo, and Ethiopia. The United States stands out as the sole representative from outside these two continents.
This distribution underscores Asia and Africa's central roles in global population dynamics. Rapid population growth in Africa is driven by high fertility rates, while Asia, despite declining birth rates in some regions, still accounts for a substantial portion of global births due to its sheer population size.
India and China: The Global Leaders
India and China, the world’s two most populous nations, contribute significantly to global birth rates. Together, they account for one in four babies born each hour. India's higher fertility rates compared to China’s reflect divergent demographic trends, with India projected to surpass China as the most populous country.
While China continues to experience substantial numbers of births, its declining fertility rates and aging population pose challenges for its long-term demographic and economic outlook.
Declining Global Birth Rates
Despite these significant numbers, global birth rates are on a downward trajectory. Factors such as urbanization, improved access to education, economic development, and changing social norms contribute to this decline.
In countries like China, low immigration rates, falling birth rates, and steady death rates are expected to lead to population declines in the coming decades. This trend may prompt shifts in policy, such as incentives for larger families or greater openness to immigration, to address potential labor shortages and economic impacts.
Implications for the Future
The concentration of births in specific regions has profound implications for resource allocation, economic development, and environmental sustainability. Regions experiencing rapid population growth will face increased demand for infrastructure, education, and healthcare, while countries with declining populations may encounter labor shortages and economic stagnation.
Understanding these trends is vital for policymakers, researchers, and society at large. By analyzing where most babies are born and examining the factors influencing these rates, we can better anticipate and address the challenges and opportunities posed by shifting demographic patterns in an interconnected world.