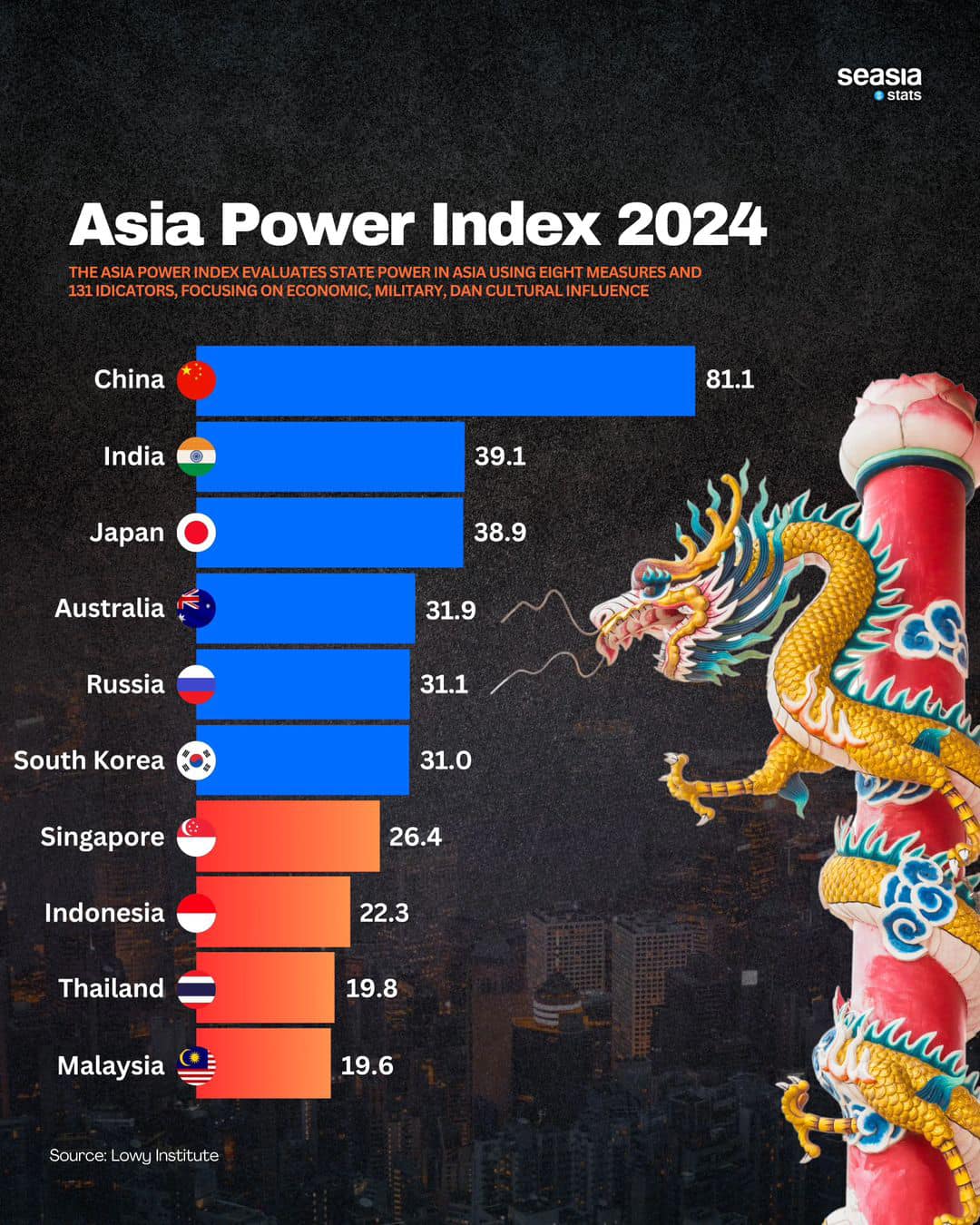
The Asia Power Index 2024, developed by the Lowy Institute, offers a comprehensive evaluation of state power across Asia. This index examines power dynamics by focusing on eight key measures and 131 indicators, assessing the influence of various countries in areas such as economic strength, military capacity, and cultural impact. The rankings provide insights into how different nations shape the regional and global landscape, particularly in an era of shifting geopolitical and economic alliances.
1. China’s Dominance: Leading the Region with an Unrivaled Score
Unsurprisingly, China ranks at the top of the Asia Power Index with a commanding score of 81.1. This positions China far ahead of its regional competitors, particularly in terms of economic and military power. China’s rapid economic growth over the past few decades, coupled with its expanding global influence through initiatives like the Belt and Road, solidifies its standing as the most influential country in Asia. Moreover, China’s military modernization and assertive foreign policy have further strengthened its regional dominance.
However, China's power is not just limited to economics and defense. Its cultural and diplomatic influence has also been on the rise, particularly through global initiatives, media outreach, and international cultural exchanges. This multidimensional approach to expanding influence ensures that China remains a key player not only in Asia but globally. Despite its dominance, China faces challenges, including economic restructuring and managing its relationships with neighboring countries, especially amid growing competition with the United States.
2. India and Japan: Balancing Economic and Military Influence
In the second and third spots are India and Japan, with scores of 39.1 and 38.9, respectively. Both countries are essential players in maintaining the balance of power in Asia, albeit with different strengths.
India’s influence is driven primarily by its large population and growing economic power. India’s strategic geographic location and its role in the Indo-Pacific region further bolster its standing in the Asia Power Index. However, India still faces significant challenges in terms of infrastructure, poverty, and internal security, which can limit its full potential in exerting influence. Nevertheless, India’s expanding role in regional security partnerships and growing defense ties with countries like the United States, Japan, and Australia contribute to its growing military clout.
On the other hand, Japan’s strength lies in its economic and technological prowess. Despite a relatively stagnant economy compared to its peak, Japan continues to exert significant influence through its technological innovations and strong alliances with the United States and other regional partners. Additionally, Japan has increased its role in regional security and defense, taking a more proactive stance in shaping the Indo-Pacific security architecture.
3. Australia and Russia: Regional Players with Global Interests
Australia ranks fourth in the Asia Power Index with a score of 31.9, while Russia follows closely behind with 31.1. These countries have notable influence in Asia, though their strategies differ.
Australia has been strengthening its position through economic partnerships and regional security alliances. Its role in initiatives like the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (Quad) alongside the U.S., Japan, and India emphasizes its commitment to maintaining stability in the Indo-Pacific. Australia’s strategic geographic position gives it an essential role in the region’s security architecture, especially as concerns grow over China’s expanding influence.
Russia, meanwhile, is a major global power, and its influence in Asia has historically been tied to military strength. While Russia’s economic ties with Asia are limited compared to other regional powers, it continues to exert influence through its defense partnerships and geopolitical maneuvering, particularly with countries like China and India. Despite challenges such as economic sanctions and internal political issues, Russia’s military and diplomatic engagements remain critical factors in its Asia-Pacific strategy.
4. South Korea and Southeast Asia: Growing Influence in Regional Affairs
Further down the list, South Korea ranks with a score of 26.4, followed by Southeast Asian countries such as Singapore (22.3), Indonesia (19.8), Thailand (19.6), and Malaysia. These countries collectively play crucial roles in shaping regional dynamics, particularly in economic integration and security cooperation.
South Korea has established itself as a global economic power, driven by its highly developed industries and technological innovations. It also has a significant role in regional security, especially with the ongoing tensions on the Korean Peninsula. Additionally, South Korea’s cultural exports, from K-pop to cinema, have gained substantial global influence, adding to its soft power in the region.
Meanwhile, Southeast Asian countries, particularly Singapore and Indonesia, have become increasingly important players. Singapore is a global financial hub with a strong economy and strategic geopolitical position, making it influential despite its small size. Indonesia, the largest country in Southeast Asia by population and geographic size, has been emerging as a critical player in regional and global affairs, thanks to its growing economy and strategic role in the ASEAN bloc.
5. Southeast Asia’s Role in Shaping the Region’s Power Balance
Countries like Thailand and Malaysia, while ranking lower on the Asia Power Index, are significant contributors to the regional balance of power. These nations play pivotal roles within ASEAN (the Association of Southeast Asian Nations), a regional organization that promotes political and economic cooperation in Southeast Asia.
Thailand and Malaysia contribute to ASEAN’s efforts to maintain peace, stability, and economic growth in the region. Both countries have developed strong economic ties with neighboring nations and global powers, making them integral to Southeast Asia’s broader strategic landscape. Their engagement in multilateral institutions and their economic policies also ensure that they remain relevant players in regional diplomacy and trade.
A Dynamic and Evolving Power Landscape
The 2024 Asia Power Index highlights the evolving nature of state power in the region. While China maintains a dominant position, other nations like India, Japan, Australia, and Russia continue to shape the geopolitical and economic dynamics of Asia. Southeast Asian countries, although smaller in influence, remain key players, contributing to regional integration and cooperation.
As global power shifts continue, these rankings provide insight into how countries in Asia are positioning themselves on the world stage. The distribution of power is not static, and ongoing economic, political, and military developments will undoubtedly influence the future balance of influence in this critical region.