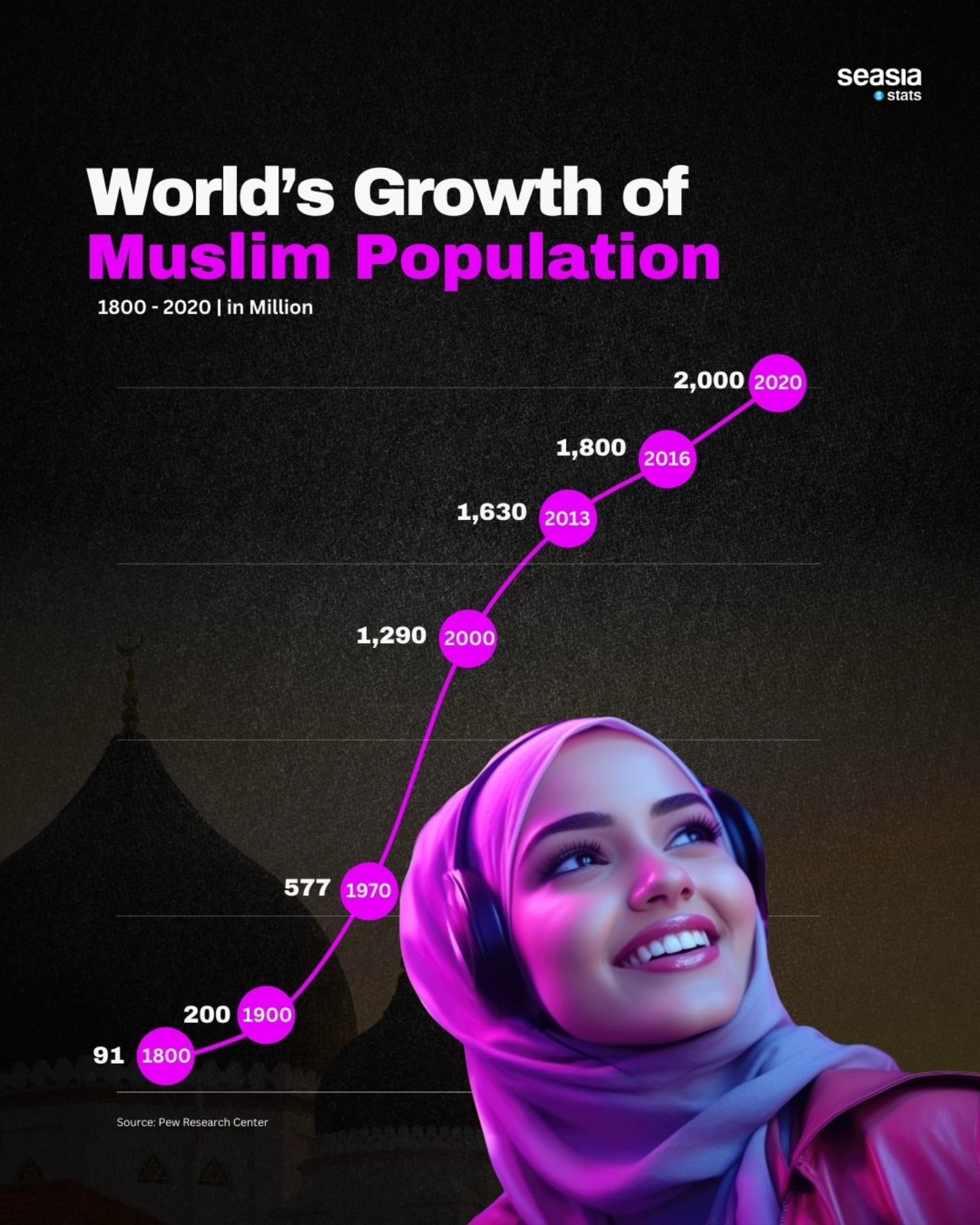
By 2030, the global Muslim population is expected to rise to 2.2 billion, up from 1.6 billion in 2010. This represents one of the most significant shifts in global demographics, underscoring the importance of understanding the factors driving this population growth. The increase is influenced by a mix of demographic trends and socio-economic factors, though uncertainties remain due to political, social, economic, and cultural influences.
Current Landscape: Where Are We Now?
Indonesia currently holds the title for the largest Muslim population in the world, with around 242 million adherents, 87-90% of whom are Sunni Muslims. This demographic dominance positions Indonesia as a key center of Islamic culture and practice. However, projections indicate that Pakistan will surpass Indonesia by 2030, becoming the most populous Muslim nation. This shift is significant, particularly for South Asia, where population dynamics are rapidly evolving, and such changes could alter the global Muslim landscape.
Key Drivers of Population Growth
Several interconnected factors contribute to the growth of the Muslim population globally:
-
Higher Fertility Rates Muslim-majority countries typically experience fertility rates higher than the global average. Cultural norms and socioeconomic conditions in many Muslim-majority regions support larger family sizes, which contributes to population growth. Family structure and community expectations play a significant role in shaping fertility choices.
-
Improved Living Standards Over the past several decades, many Muslim-majority countries have seen significant improvements in healthcare, nutrition, and general living standards. Economic development in regions such as the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and parts of Africa has led to increased life expectancy and reduced child mortality rates, both of which contribute to population growth.
-
Access to Education Education is another key factor influencing population trends. Increased access to education, particularly for women, has been a game-changer in many Muslim-majority nations. Higher educational attainment often correlates with delayed marriage and childbirth, as well as smaller family sizes. As educational opportunities expand, particularly in rural and underserved areas, fertility rates are expected to gradually decline, reflecting the broader global trend of women in more educated populations opting for fewer children.
Projections and Future Trends
The global Muslim population's projected increase to 2.2 billion by 2030 comes amid a changing socio-political and economic landscape. While the factors driving growth are clear, the rate of change in fertility and educational access will determine the pace and scale of this demographic shift. Furthermore, countries such as India, Bangladesh, and Pakistan will play critical roles in shaping the future composition of the Muslim world, given their large and growing populations.
This demographic change also carries significant implications for social, economic, and political development, with Muslim-majority nations potentially experiencing shifts in global influence. Understanding these trends will be crucial for policymakers, businesses, and international organizations working within or engaging with these regions.
In summary, while the global Muslim population is poised for substantial growth by 2030, this trend is influenced by several factors, including higher fertility rates, improved living standards, and educational advancements. These developments will reshape the Muslim world and have broader implications for global demographics in the coming decades.